Managing Container
by Hasan
Week Plan
- Amazon Elastic container Service (ECS) basics
- Components
- Task Management
- Demo
Orchestration
- Multiple container for resiliency
- We spread applications instance host, availability zones and even AWS regions
- Multiple container for Scalability
- Containers are ephemeral
- Normally ephemeral means lasting for little amount of time
- If Application have static asstes, it should be pulled from storage platform, if our application have transactional data that should be read from to and written to an external database.
- Networking
- Authenticate and integrate to storage and database.
-
New containers also need logs
- There are some platforms which does all of the hard work for us, these are called Container Orchestratin Platforms
- These platforms helps the container spinning them up and down, making sure wire up the network to specifications, handling permissions, sothat certain containers only communicate with other containers which they need to or allowed to and providing integration with other services such as storage, databases messaging queues, centralize logging and monitoring and many more.
- This week we will be analyzing such orchestration service.
Amazon Elastic Container Service (ECS)
Elastic Container Service (ECS)
-
mainly broken into two pieces
-
Control plane Responsible for provisioning software, any user or service requested configurations, and managing the lifecycle of resources. They are also responsible for helping the data plane do its work
-
Data plane Provides capacity so that it can run whatever work control plane tells us it needs to.
- Analogy: Boss tells us to do something. Boss provisions the task to us and helps manage the lifecycle of the task. We are doing the job is the data plane as we generally perform the task what our boss already said to us
-
- When you first use
ECSa default cluster is created for you. They can create additional cluster for your work load, as it fit. -
Inside these clusters are
EC2instances, which you can customize and control, that simply act as docker host. This is often we refer to as data plane.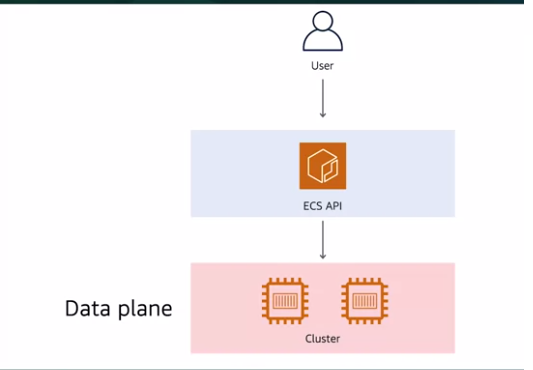
- A Data plane gives the power so that the container can actually run.
- In the top level there is API, giving high level commands to this API, is how you interact with your cluster.
- So if you tell API you need to run four copies of particular container distributed across three AZs, the API will find a way to place those containers on instances across all three availability zones.
- Actually
ECScompletely takes care of cluster management as well as coordination and automation of the deployment of the container. - What allows you to interact with containers that is control Plane
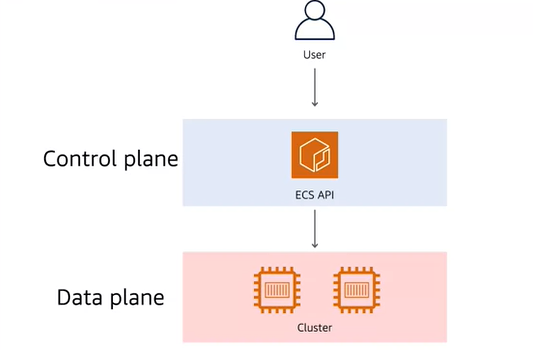
Contrl plane here can be said that as a ECS service itself, as it orchestrates on your behalf and provides an entry point for commincation through the API
## Summary of ECS
- ECS the service and conrol plane communicates with EC2 instances in your cluster to start, stop and monitor your containers as you send request through API.
- The ECS contrl plane agian abstracted away from the customers through the use of API.
- But the customers still have the responsible over the data plane, as they are still accountable to EC2 instances.
- But the abstration of Control plane is ther true beuty of ECS
## ECS components
-
Task defination –> text file in json format that describes one or more containers thar form your applications with a maximum of 10. ### Definations
- Task –> Task instantiation of task defination wihin a cluster
- Scheduler –> places a task on the cluster.
- Cluster –> logical grouping of computer resoureces. clusters can be managed for you using fargates or managed by you using EC2 instances.
- Service –> runs and maintains a specified number of instances of a task defination simultaneously Can be run behind the load balancer allow you to specify deployment configurations and can be deleted which would stop all of the running tasks associated with the service.
- Agent –>runs on each compute node within the
ECScluster. It sends the information about the resources current task and resources utilization on ECS as well as start and stop tasks whenever it recieves information from ECS
Scheduling and Task Placement
- Generally to launch a container there are couple of options
- Do it manually –> scalability is problem
-
In ECS Scheduling task and placing task are handled by two separate engines
- Scheduling Engines
- Placing Engines
## Scheduling Engines
Scheduling Engines whole goal is to provide logic how, where and when to install the containers. So you specify which task defination to start, and schedule Engine will make the necessary calls to control plane to start that task on a specific instance or intances.
ECS has different type of schedulers
- one type of
Amazon ECS Service Scheduler- Service Scheduler allows you how you want to run your task and how many of copy of tasks you want to schedule. Suppose you want 5 copy of task running. Service scheduler make sure that 5 copy of tasks always running if one fails then service scheduler create another and makes it running.
- Also allows
Daemon ScheudlerDaemon Scheduler makes sure a specific task always running in specific cluster. Monitoring or logging task.
- Another type of scheduler is
Cron Scheduling using Amazon Eventbridge- this will run a specific task on specific time, may be business hour.
- Other option for scheduling
- Create scheduler
- Leverage third party scheduler
- Run task manually
## Placement Engine
- Place task where appropriate memory and CPU space is available and also a configuration based on user choice.
- First engine look on task placement constraints.
- what should run together or what shouldnot run together (high cup needed 2 processes should not run together)
- Strategies allows you to choose how to place your task.
- densely packed task across instance for cost minimization
- spread your task across instances
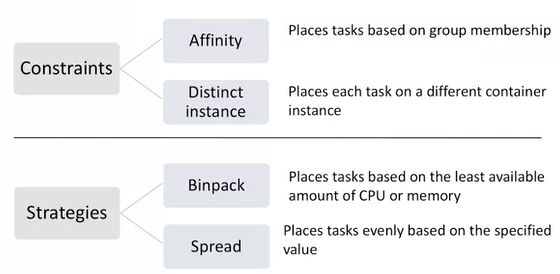
- Strategy chaining is also available means two things together, pack task densely and minimum cost.
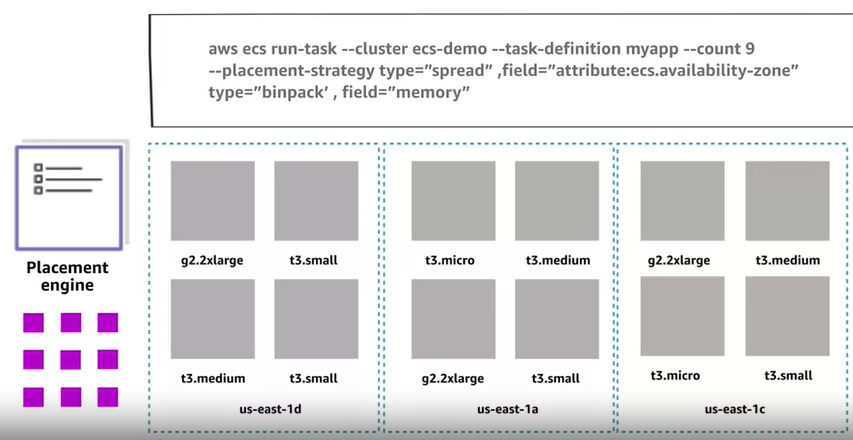 Here in the iamge command we can see that placement strategy combined with binpack
Here in the iamge command we can see that placement strategy combined with binpackECS Demonstration
- Creating an ecs cluster and the name of the cluster is setup ECSDemo
aws ecs create-cluster --cluster-name ECSDemo
In the command the cluster arn can be found means cluster already created
- We now need to create an EC2 instance and passing information for that instance
aws ec2 run-instances --count 2 --image-id ami-0f161e6034a6262d8 --instance-type t3.medium --key-name ecs-container-instance-kp --subnet-id subnet -0b745a2448d91131 --secuirity-group-id sg-0aae6caa0b11ff6db --iam-instance -profile Name-webappserver --associate-public-ip-address --user-data file://userdata.txtamiid the latest ECS optimized ami where ECS agent and docker agent will be installed, therefore no necessary to install themuserdata.txtwill be availble on folder. User data will be executed when first time EC2 instance will be started first time.#!/bin/bash echo ECS_CLUSTER=ECSDemo >> /etc/ecs/ecs.configIt actually creating a configuration file which will tie with cluster
- Now we will create task defination
aws ecs register-task-defination --family python-app --task-role-arn arn:aws:iam::832211724792:role/PythonECSTask --execution-role-arn arn:aws:iam::832211724792:role/ecsTaskExecutionRole --network-mode brridge --container-defination file://container.jsonWe can have a look on the contanier.json
[ { "name": "webapp", "cpu": 100, "memory": 100, "image": "832211724292.dkr.ecr.us-east-1.amazonaws.com/pythonwebapp:latest", "portmapping": [ { "protocol": "tcp", "containerPort": 8080, "hostPort": 80 } ], "essential": true } ] - Create the service which will use this task
aws ecs create-service -cluster <cluster-arn> -service-name ECSService --task -defination <task-def-arn> -desired-count 2 --launch-type EC2 --scheduling-strategy REPLICA -deployment-controller type=ECS - Service is launched we should describe the service
aws ecs describe-service --cluster ECSDemo --service ECSService - Now we want to list those tasks
aws ecs list-tasks --cluster ECSDemo --service-name ECSServiceSo we are capable seeing task arn name in command line We will describe those task and find out what EC2 instances on running those task and find out public DNS name from EC2 instances and access the website.
-
aws ecs describe-tasks --cluster ECSDemo --task <task-arn>8.
aws ecs describe-contaniner-instances --cluster ECSDemo --container-instances <container-instance-arn> - Next we need to describe EC2 instance which we called our container instance. We need to grab instance-id
aws ec2 describe-instances --instance-id <instance-arn>From the output we should get Public DNS name and paste it into browser, this should be avialable now
Normally in the app used dynamodb and in the app no configuration file or environment variable is defined. The credential is found the iam role. Normally first search for environment variable or configuration file or iam role. IAM role is more secure
Also in case of database management, for example if any password needs to be changed then it is probelem. In AWS there are some solution available
AWS Secret Manager** Donot use AWS access key id instead use iam role
SPOTFleet–for saving money