Kubernetes
by Hasan
Basic Kubernetes objects
- pods
- Services
- Volumes
- Namespaces
Pod
- A container or group of containers you want to run
-
It actually a wrapper around your container which Kubernetes communicates for management.
- Pod can have one or more containers. If some containers are tightly coupled or related you may choose to tie them in a single pod. Normally one pod for single container is most common.
- Each pod has ip address
Service
- A pod or collection of pods you want to expose as microservice
Volumes
kubernetes object that represent directories that mount to pods so containers have access to read and modify files in a persitent manner.
Namespaces
Allow you to have multiple virtual Kubernetes clusters backed by the same physical cluster.
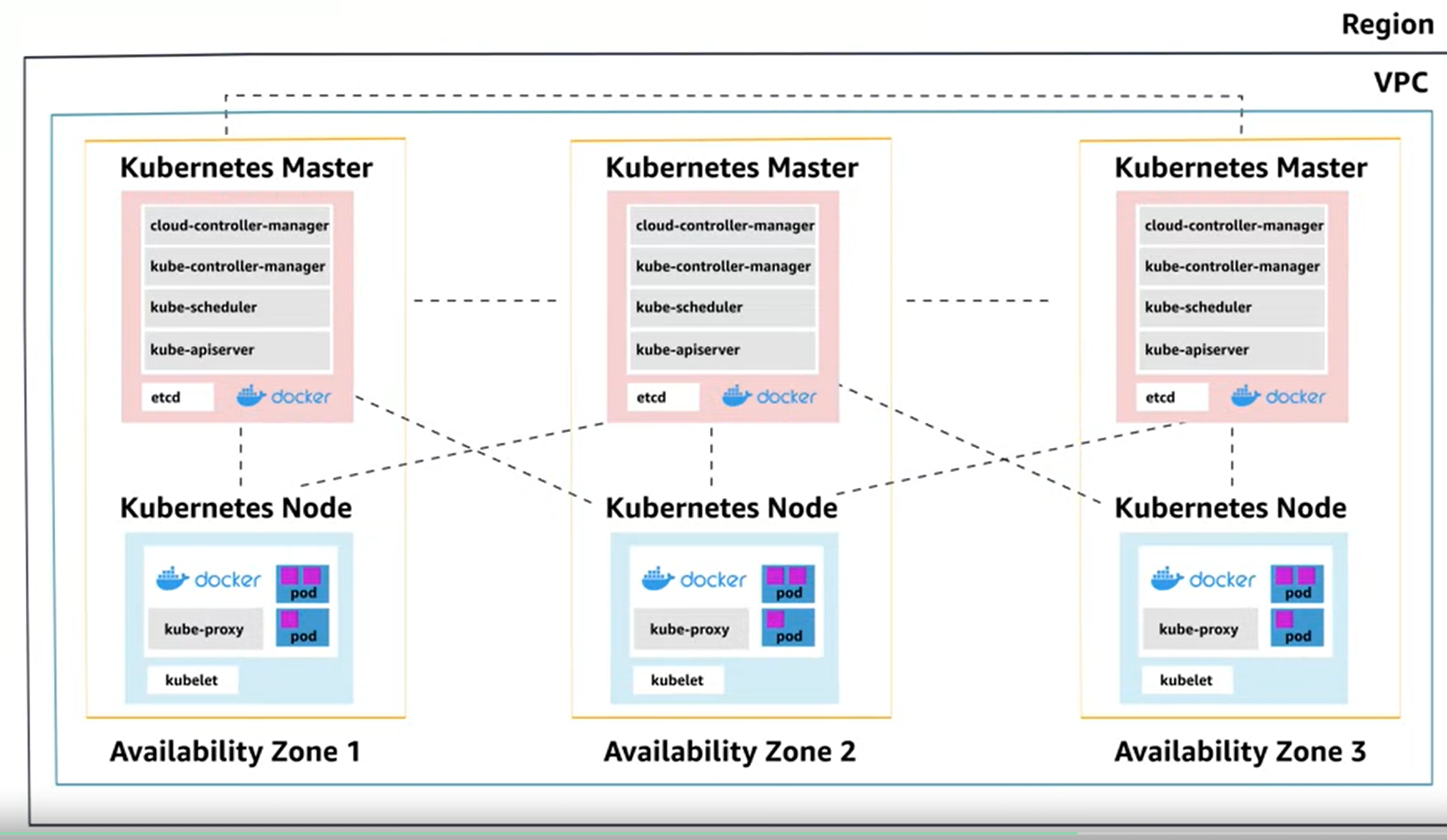
Amazon EKS Demonstration
- EKS and kubernetes command line tools(EKS control und Kubecontrol) installation
- EKS control will be utilzed for cluster
- Kubecontrol will be utilized for container
ekctl create cluster \ > --name ekddemo \ > --version 1.14 \ > --nodegroup-name standard-workers \ > --nodetype t3.medium \ > --nodes 3\ > --nodes-min 1 \ > --nodes-max 4 \ > --nodes-ami auto
node ami –>image for containers node information related to the node that will be launched as a part of the cluster
- First see the cluster which was just created
aws eks list-clusters --region=us-west-2 --output=json - Nginx image will de extracted from docker-hub creates a deployment for one pod
kubectl create deployment nginx --image=nginx:latest - In real world we don’t user latest and we need more than one . Now we can scale up
kubectl scale deployment/nginx --replaces=4
here it is scaled to 4 pods
- Now we will describe the pod to get more details
kubectl describe deployment/nginx - Now let see the pods
kubectl get pods - Now we will expose the pod using load balancer
kubectl expose deployment/nginx --port=80 --target-port=80 --type=LoadBalncer --name=webservice "web" exposedkubectl get svc/web -o=jsonpath="{.status.laodbalancer.ingress..hostname}"
Scaling with k8
- kubernetes use nodes and pods both needs to be austoscaled.
- EKS
cluser autoscalar- pods failed becuase of insufficient cluster resources. Nodes will be added in that case.
- Underutilized nodes on cluster
- Cross zoning not possible. Therefore needs to inform/configure to aware of autoscaling groups then command line interface can be used (kuberctl)
- Pod autoscalar
Horizontal Pod autoscaling- The metric used for this autoscalar is
kubernetes metrcis server Custom metric APIcan be usedVertical pod autoscaler
- The metric used for this autoscalar is
Kubernetes Ecosystem
- Portable and extensible. To run it in AWS there are some options
- Done by ownself–> atleast 3 master nodes are required–> complex
- Amazon Eks (elastic kubernetes service)
- Synchronization of masters
- Automated version upgrades and patching of master
- Handles high avialability