Introduction_ml_in_production_week2
by Hasan
- This is class notes of week 2
- First week class lecture
Selecting and training a model
Modelling overview
- This week we will be focusing on Modelling part of the Modeling cycle
- We have two Approach
- Model centric
- Data centric
- We will not just try to improve Neural Network architecture but we will try to get more clean data.
- That does not mean we will wait to get more and more data, which is very expensive. We will try to get tool, which helps us to get more cleaner data.
Key challenges
AI systems = Code + Data
-
Normally code (algorithm) from github normally is ok. The problem is mosto of the time is data.
- Algorithm/ Model
- Hyperparameters
- Data
Model development is a iterative process
- Model + Hyperparameters + Data –> trianing –> Error Analysis
- Before roll out to production Error Analysis –> Audit performence
#### Challenges in model development
- Training set doing ok
- Doing well on dev/test set
- Doing well on business metric
Why low average error isn’t good enough
1. Performence on disproportionality examples
- Example websearch
- Inforamtional or transactional queries
- Apple pie recipe
- Wireless data plan
- Diwali festival
- Latest movies
- Naviagational queries
- Stanford
-
Youtube
- In case of Naviagational queries users normally are not forgivable.
- There is a possible that your test test accuracy is higher but you can only detect some navigational query. Then it is not good for business
- You can do to weight one category, it works in some case but not always.
2. Performence on key slices of the dataset
- Example: ML for loan approval
- make sure not to discriminate by ethnicity, gender, location, language or other protected attributes.
-
Only test set accuracy but if there is some bias, then it is not acceptable to roll out it in production.
- Another example: Production recommendation from retailers
-
be careful to treat fairly all major user, retailer, and product categories.
- how to spot and address potential problems like these we will learn later.
3. Rare classes.
- Skewed data distribution
- Accuracy on rare classes Hernia is rare and performance is worse (0.851). Overall accuracy was not bad, but with ignoring Hernia is not acceptable.
Establish a baseline
Unstructured data
- baseline : Human level performence( HLP) to compare which was previously detected by human.
- and then compare with it actual baseline.
Strucuted data
- HLP is not useful baseline.
Ways to establish a baseline
- Human level performence (HLP)
- Literature search for SOTA/ open source
- Quick and dirty implementaiton.
- performence on older systems.
Tips for getting started
Iteration proces
- Model + Hyperparameters + Data
- Training
- Error Analysis
- Audit performance
After doing above process continuously we can reach to our goal
- Tips for the first step
- Literature search to see what’s possible (courses, blogs, open source projects)
- Try first simple which is doable.
- Find open-source implementations if available.
- A reasonable algorithm with good data will often outperform a great algorithm with no so good data.
Deployment constraints when picking a model
Yes. if Baseline is already established and you are sure this project will work.
No. If purpose is to establish a baseline and determine what is possible and might be worth pursuing. If the open source implementation is so complex that you will never implement that.
Sanity check for code and algorithm
- When trying first time, before trying all data, try with small data, may be only 1 training example.
Error Analysis and performance auditing
-
Spread sheet Example | Label | Prediction | Car Noise
—- - May be come with new ideas.
-
May be in most of the error you see there is a low band with connection, and you added new column named as Low Bandwidth in spread sheet
- This spreaad sheet helps you to see the source of the error and where to put attention.
- There are some tools like
__landing lens__
Error analysis is also an iterative process
Useful metrics for each tag
- What fraction of erros has that tag ?
- of all data with tht tag, what fraction is misclassified ?
- What fraction of all the data has that tag ?
- How much room for for improvement is there on data with that tag ?
Data iteration
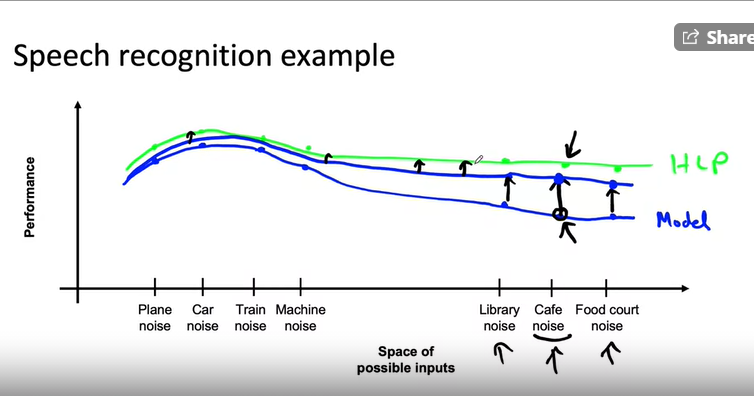
- It is like rubber band, if you increase the data of some type means, the you pull the rubber band, and subsequent places which is near to this point also goes up.
- But not the point which is further. However after increasing the data point may be the point will move and you need to concentrate on different point, which can be found by error analyis.
Data Augmentation
- Create realistic examples
- the algorithm does poorly on but
- humans (or other baseline) do well on.
Check list
- Does it sound realistic.
- is the x -> y mapping clear ? (e.g. can humans recognize speech ?)
-
is the algorithm currently doing poorly on it?
- Sometiemes Photoshop also helps also image augmentation.
Can more data hurt ?
- if unstructured data
- model is large.(low bias)
-
the mapping (x->y is clear, human can detect) Then adding data rarely hurts.
- if model is small may be hurts.
- if x-y map changes. if augmentation sometimes changes, rare. but one should consider.
Strurctue data ?
- Additional feature addition helps.
-
may be whether a person vegetarian ( not always hard 0 or 1 may be soft(like 0.6 or 0.1)), how much vegetables are oredered in their menu.
- Ask a question what are the feature that can help make decision ?
Adding Feature.
Shifting is going on like below
- Collaborative filtering –> Content based filtering.
- cold start problem : if no data is availble how to recommend them ( not people like him recommendation but see the actual feature of those recommendation)
(similarity) (Content description of the restaurant) cold start feature
- model-> training-> Error Analysis (feature addition.)
Data iteration.
-
Start training a model –> training –> Error analysis
-
Error analysis is harder for structured data to compare to ( such as HLP)
- Error Analysis can help ideas to improvement or may be find any tag for imporovement.
- Then do iteration again from starting to modelling.
- Features are also form of data, so error analysis can help to do modelling.
Experiment tracking
What to track
- Algorithm / code versioning
- Dataset used
- Hyperparameters
- Results
Tracking tools
- Text files.
- Spreadsheet
- Experiment tracking system( Weights and bias).
Following things needs to be remember when searching for tools for experiment tracking.
- Information needed to replicate the results ( internet is problem)
- Experiment resuls and with summary metrics /analysis
- Perhaps also: Resource monitoring, visualization, model error analysis
From Big data to good data
- Try to ensure consistency high-quality data in alll phases of the ML project lifecycle
Good data
- Covers important cases( good coverage of input x)
- Is defined consistency (defination of y label is unambigous)
- Has timely feedback from the production data(distribution covers data drift and concept drift).
- Is sized appropriately.