Introduction_to_machine_learning_to_production
by Hasan
Week 2 Introduction to Machine learning in Production 3 week
- This is class lecture of the 3rd week
Define Data and Establish Baseline
Why is data defination hard ?
- different labellers can detect different boxes. It is OK to use same labellers data, but if algorithm uses $1/3$ from one labeller and other from other labeller, then it is a problem.
- The upper problem introduces
label consistencyproblem in algorithm.
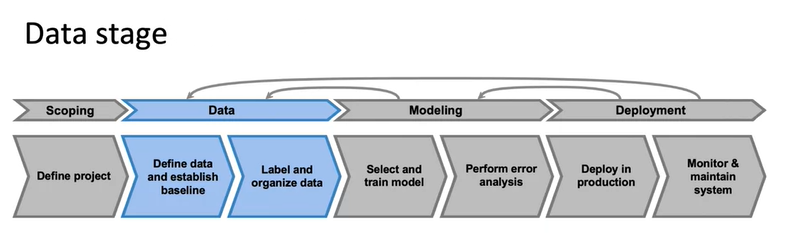
- In this week we will be working on data part of the machine learning pipeline.
- what is x and y and how to make consistent label
More label ambiguity example
-
In a speech recognition example, may be after listening a speech, different labellers label that in following manner.
- Um, nearest gas station
- Umm, nearest gas station
- Nearest gas station [unintelligible]
-
Lets see some structured data problem
- User ID merge example.
- Ask human labeller from human judgement to label data.(very ambiguous)
-
Some more ambigous example in structure data
- Whether is a bot or not
- whether is a fraud
Data Defination questions
- What is input x ?
- Lightning ? Contrast ? Resolution ? ( if possible improve this situation in input x)
- What features need to be included ?(in structured data)
- What is the target label y ?
- How can we ensure labellers give consistent labels ?
Major types of data problems
- We have different types of machine learning problem.
- Structured and unstructured or small data or large data.
- It is difficult to differ from small and big data. Normally as rough estimate one can tell if there is less than
10000example, then it is small data problem, and vice versa. - Actually it is a fuzzy limit, The reason Andrew use this, it is very painful to manually check every example if the number is more than that.
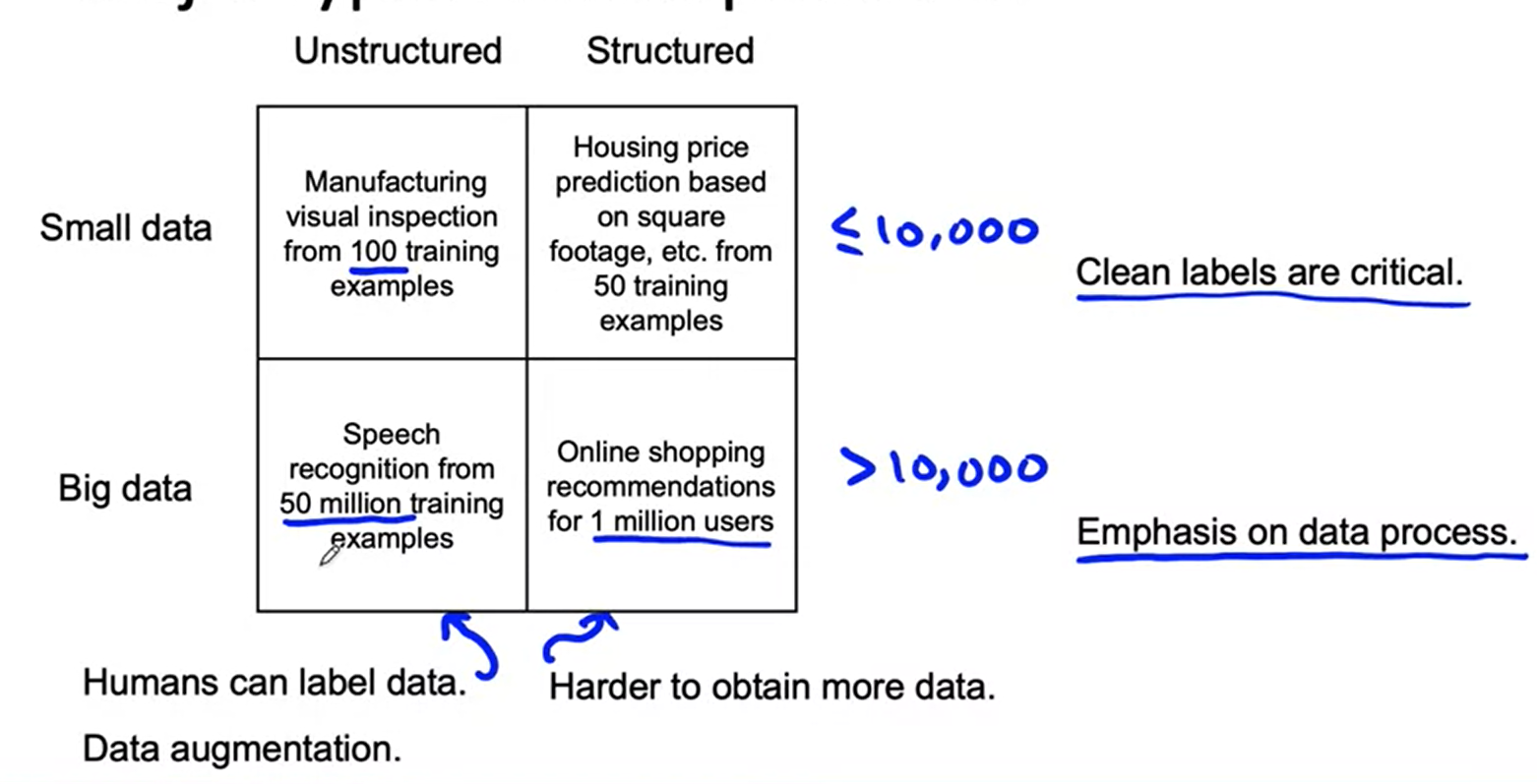
-
Above picture summarise the data differences for structured/ unstructured data and small/big data.
- Unstructured data, data augmentation help or use some more human labellers.
- Structure data it is difficult to get more data.
- In case of small data, clean data is very important.
- In case of big data, clean data is also very important. However, emphasis on data process, how data is collected, how the rules for labelling is defined.
Summary for unstructured/structured data
Summary for small/big data

-
In case of big data, it is not possible to talk with all of the labellers, may be talk with small amount of people and tell them to make a rule and inform all of the labellers
-
If anyone want to take advice or want to hire machine learning engineer, it is good to take advice or hire the people who already worked on the quadrant.
Small data and label consistency
- In case of small data, if there is noise in the data, then it is difficult to predict the function. e.g. predict speed of the helicopter from voltage.
- If there is lots of data available but there is a noise, it is not very problem to predict the function.
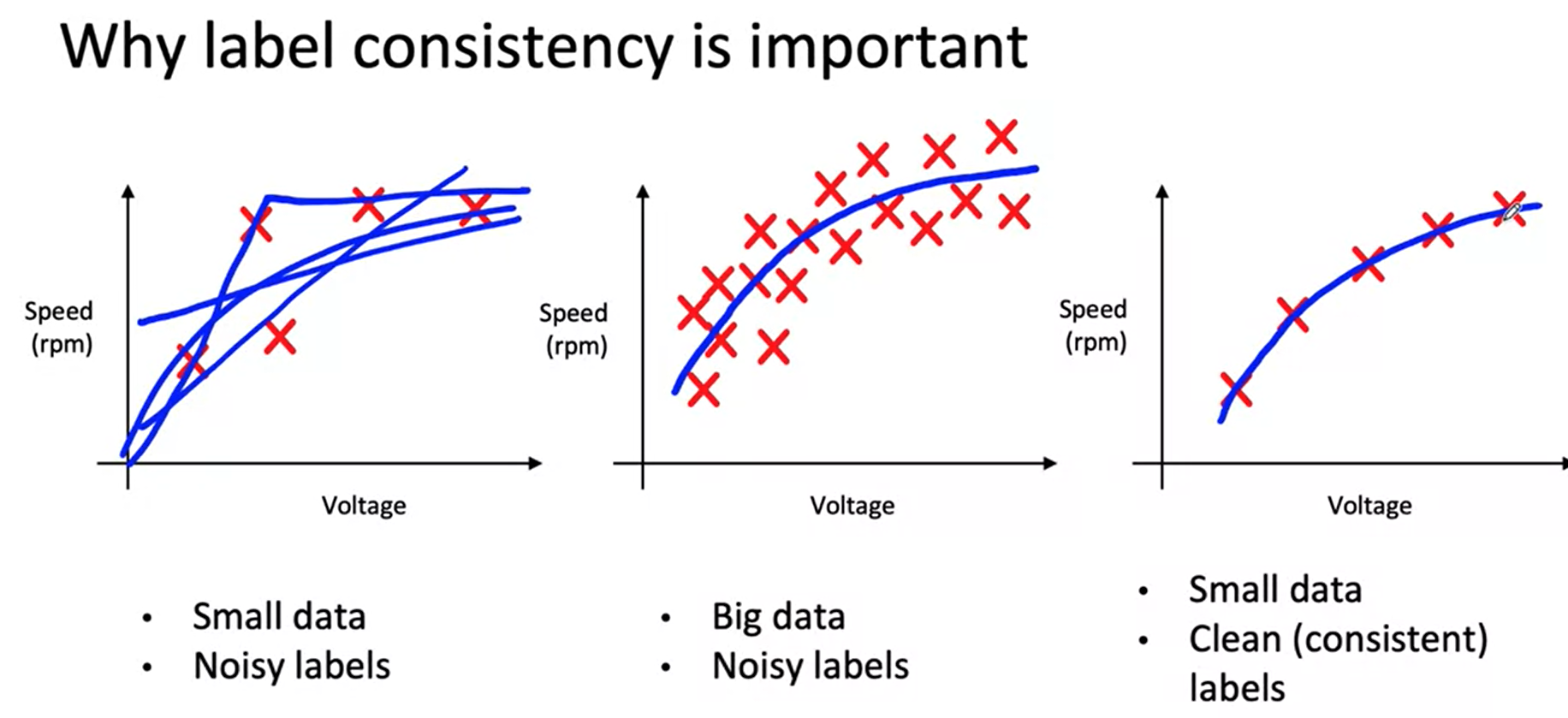
- Andrew already created computer vision problem, where there is just 30 example and it works fine, the key was clean data.
- Another example, if there a computer vision problem, where the task is to detect scratches in phone.
- If it is not defined, what is the size of defect for small and big scratches, then there will be inconsistent labelling.

- Summary: label consistency is important for small data, for big data there are some criteria where small data is available, in that case for big data also, label consistency is important.
Improving label consistency

-
Standardize or merge labels if possible
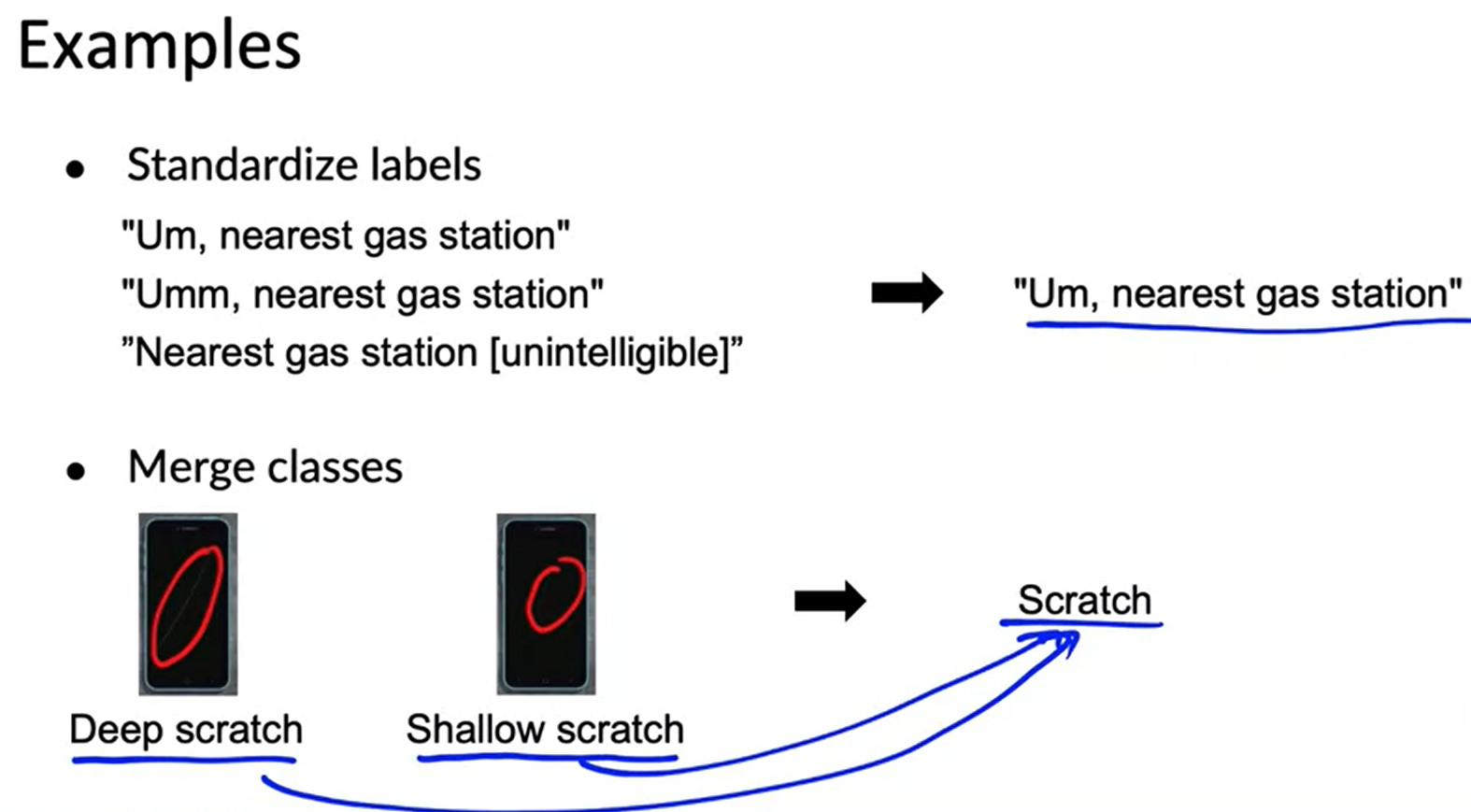
-
Or create another label to detect uncertainty.

- from above phone detection case we can change number of class from 2 to 3, 3rd class will be uncertain.
- Or from speech recognition problem, create another class for unintelligible could be helpful for label consistency.

- In big data the 3rd case, Andrew think it is overused in machine learning. However we can first make sure first 2 points are OK, then we can do the 3rd case
Human label performance (HLP)
- If business owner needs 99% accurate model, try to see HLP and then say the business owner what could be possible.
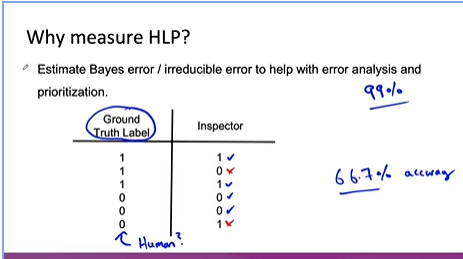
-
Actually there is a question, whether we are measuring what is possible, or we are measuring two different humans performence difference.
-
let’s consider the application of HLP.

- The goal is not beat human but to raise the human level performance
Raising HLP


Label and Organize Data
Obtaining data
- How long should you spend obtaining data ?
- Let say training 2 days
- Error analysis 2 days
- In this case Andrew will urge not to spend 30 days to get the data
- And get the data iteration loop as early as possible.
- May be only 2 days to collect the data and start as early as possible. May be 2 days is too short.
- Then you can go later more data after doing error analysis.
- One exception would be where you have worked with the problem before and you know certain amount of data is necessary for this type of problem, may be then you can wait until the amount of data fully available.
- If this is a new problem, then start as early as possible with the problem, then if necessary come again to collect more data.
Inventory data
- Before collecting data, it is a good practise to do some brain storming, saying what are the data sources available and what are the relevant cost getting those data.
- One thing which is very important but missing most of the time to consider the time, getting from those data sources.
- Other factors to consider
- Data quality
- Privacy
- Regulatory constraints
Labeling data
- There are some options to get the label.
- In-house
- Outsource
- Crowdsource
- Having Machine learning labeller labelled data is expensive. But doing this for small amount of time is usually fine. When Andrew start a project, he try to spend some time to label by himself, because it helps him to get intuition about the problem.
- Who is qualified for labelling ?
- Speech recognition: any reasonably fluent speaker.
- Factory inspection: medical image diagnostic- SME (Subject matter experts.)
- Recommender system: may be impossible to label well.
- Another tip: If you have say 1000 example, you want to have more data, how much more data is needed?
- Andrew said not to get more data than 10x at a time.
- After that carry out error analysis, see the performance on them, and then try to increase the data.
Data pipeline
- Normally from raw data to ML process there required some pre-process.
- After that the preprocessed data requires to go ML algorithm.
- How to make sure, that your preprocessing is repeatable or you can have same type of preprocessing which was used during development.
- Spend less time during POC phase

Meta-data, data provenance and lineage
- If we have a data pipeline like the following
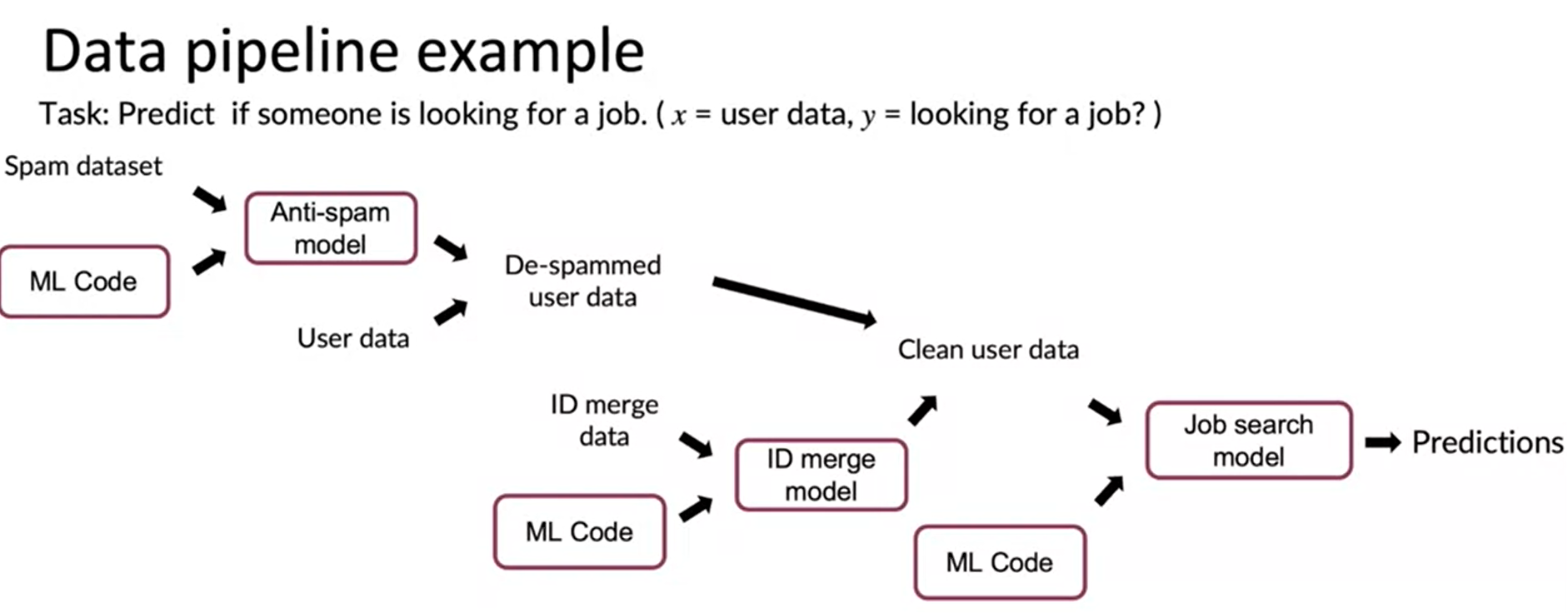
-
The arrow sign shows information flow direction and purple represents code
- Now after some time may be after one month you found out there was a error in your code.
- How you do you go back and fix this problem, specially each of the system is devolved by different engineer.
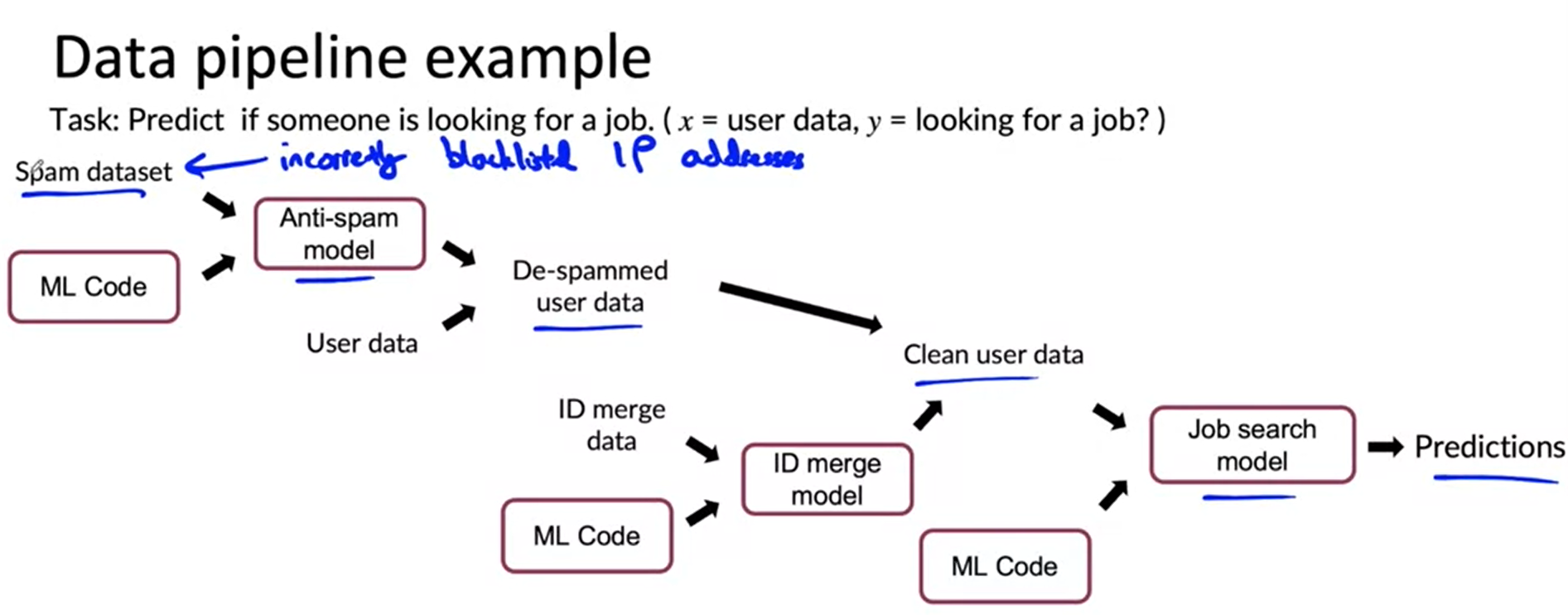
- One thing that helps is to keep track of
- Data provenance ( where the data came from)
- Data Lineage (Sequence of steps)
- Expensive documentation can help
- But in Production step there are MLops tools which will help you maintain data provenance and lineage.
- Andrew think these tools have a huge place for improvement.
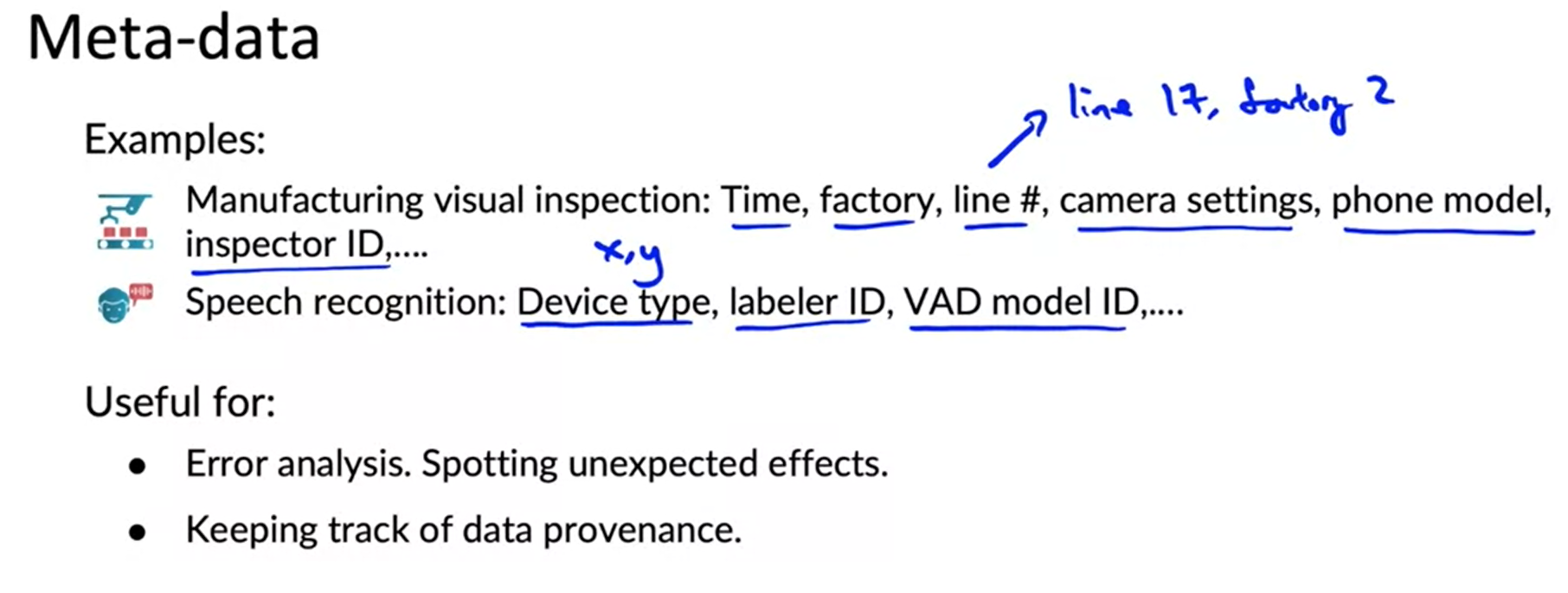
Meta data
- keep track of meta data helps for error analysis and also maintain data provenance and lineage.
- It is harder to comment the code later. Same thing if you don’t save meta data in time, then it is quite hard to save meta data later.
Balanced train/dev/tes splits
- Normally done Random split
- In case of small data, balanced train/dev/test is very important
Scoping (optional)
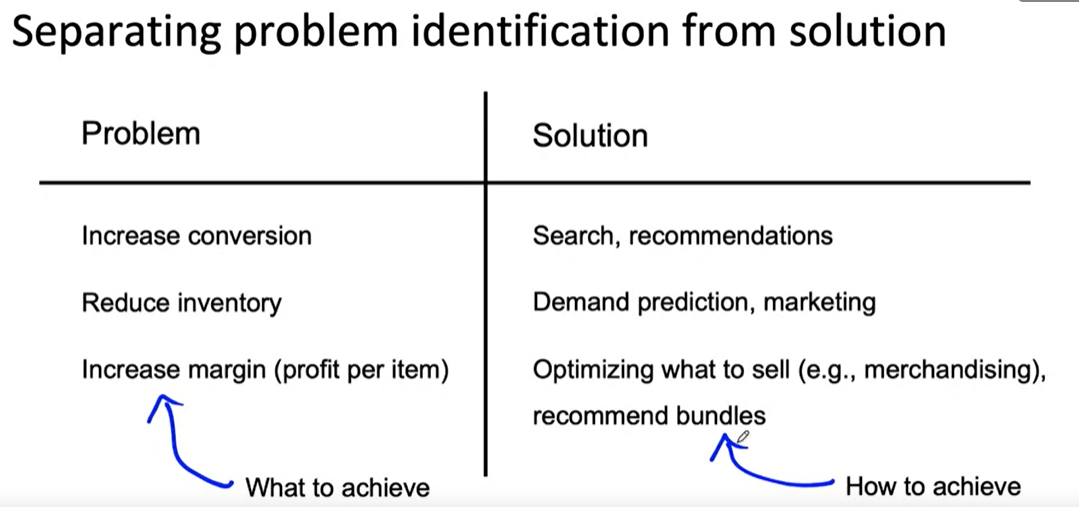
What is scoping
- Where to spend time or promising project
- After brainstorming may be get lots of ideas.
- What we need to consider

- How to say which one is very valuable than other project ?
Scoping process
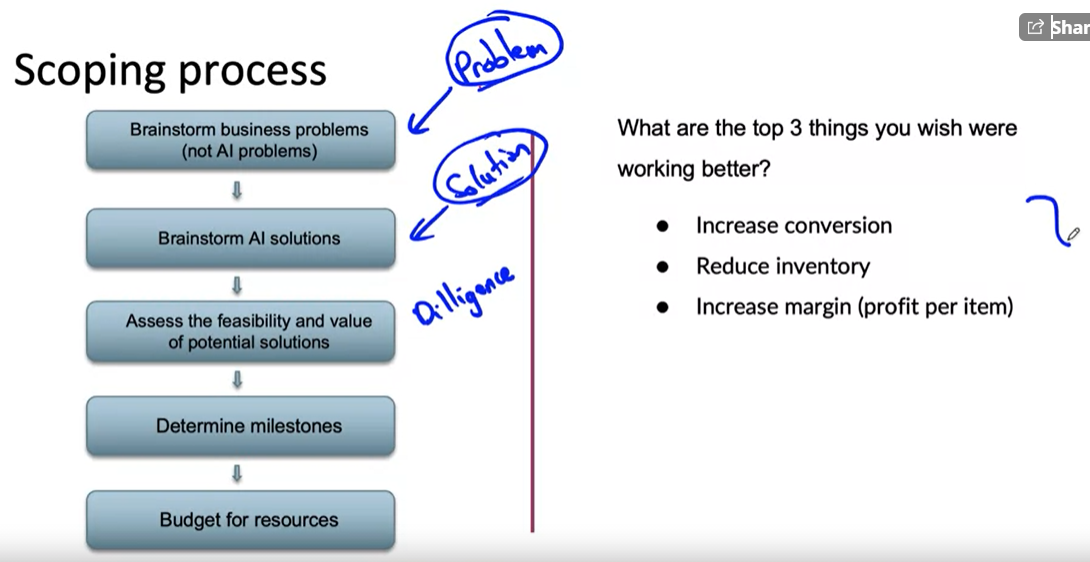
- As a first step, need to brainstorming
Diligence on feasibility and value

- Here we have used three concept
- HLP
- Predictive features are available
- History of project
- For human level performance make sure whether a human can detect that by watching simply the image not when he was there physically.
- Do you think there is a predictive feature available in the x, is very important step.
- History of project
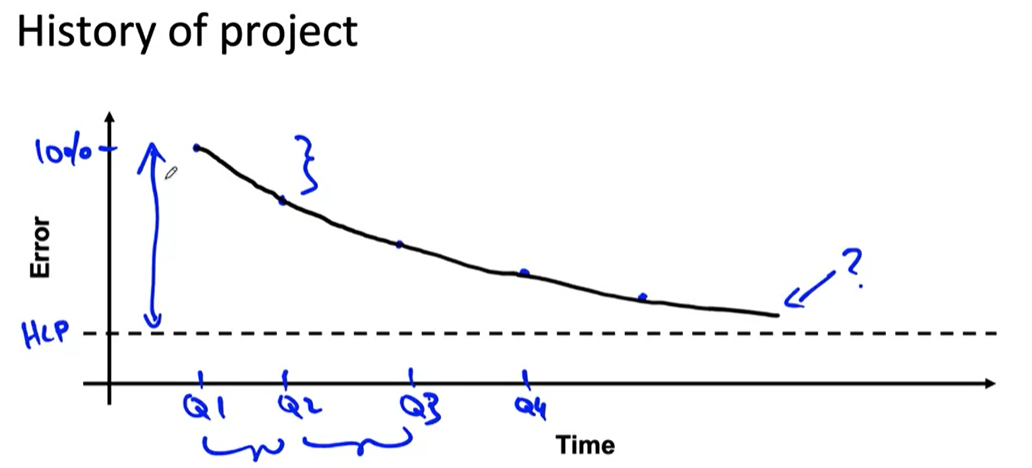
- By watching the history say every 6 month and how error is shrinking, you can say something, whether it is valuable to spend time to decrease the error.
Diligence on value

- Try to be far from the comfort zone of the metric both ML Engineers and the business people and try to agree on a metric.
- If we somehow do back profiling or do Fermi estimate, how Ml metrics correlate with business metric, may be this would be a nice agreement.
- Need to consider Ethical consideration.
Milestones and resourcing
